Borrowers with scores of 661 or higher are 66% more likely to get a car loan than those with lower scores, but there are options for those with lower scores.
Financing a car is a huge financial step, and knowing your credit score can help you get a financially attractive deal. A third-quarter 2022 report released in December by credit bureau Experian shows that the average credit scores of people financing vehicles rose slightly from a year ago.
This report also found that on average, according to the data, the credit score for a used car loan or lease was 678, while the average score for a new car loan or lease was 738. The report also shows that 66% of cars financed were for borrowers with credit scores of 661 or higher. About 14% of the financing went to people with scores between 501 and 600, and about 2% went to people with scores below 500.
A lower credit score won’t necessarily keep you from getting a car loan, but it might lead to a higher interest rate, which can make it harder for you to afford the payments. In general, having a larger down payment, shopping around for financing and bringing in documents showing a good payment history on other big purchases may help you offset damaged credit.
Better Credits, Lower Costs
Interest rates vary based on your credit score, so knowing what you can expect to pay for a car can help you budget for that purchase. A target credit score of 661 or above should get you a new-car loan with an annual percentage rate of around 4.90% or better, or a used car loan of around 5.47% or lower.
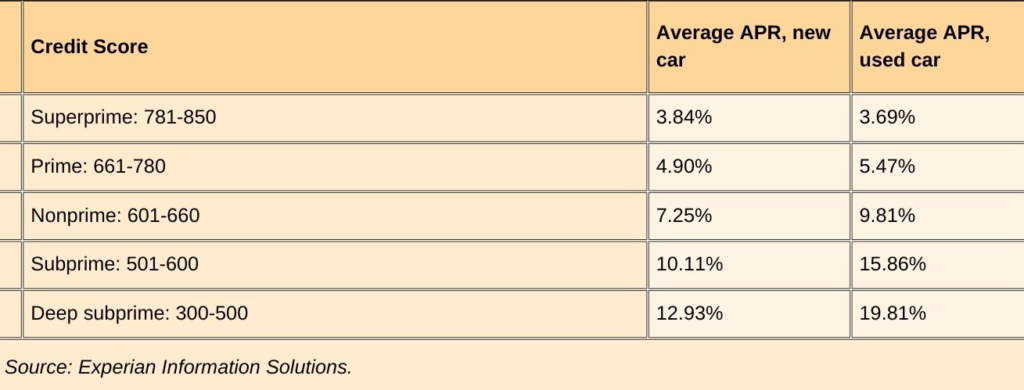
According to Experian data, a buyer with a score in the low 700s might see rates on used automobiles of around 5.47%, as opposed to 15.86% or more for a buyer with a score in the mid-500s. The difference that can create is seen by using a car loan calculator.
For instance, a buyer with a higher credit score would make a monthly payment of roughly $382 on a $20,000, five-year used automobile loan with no down payment compared to a buyer with a lower credit score who would make a payment of $485. Over the course of the loan, the buyer with superior credit would pay roughly $2,904 in interest, but the buyer with less-than-perfect credit would spend around $9,105. Additionally, in most jurisdictions, having negative credit can result in higher auto insurance costs.
For new auto loans, the variations aren’t quite as pronounced: applicants with credit scores in the low 700s may anticipate an average rate of 4.90%, while those with credit in the mid-500s can expect to pay 10.11%.
FICO auto score: What is it?
It’s a good idea to check your credit score in order to have a sense of what dealers may find when they review your credit record. However, it’s likely that your dealer will utilize a FICO automotive score rather than a standard FICO score or VantageScore.
Your FICO auto score is a specialized number that ranges from 250 to 900 and gives more weight to past vehicle loan repayments than the standard FICO score does. Additionally, it gives any repossessions or bankruptcies you may have previously filed related to auto loans more weight. You can get a whole set of FICO scores at myFICO.com to examine your automobile score and then terminate the service to avoid paying the comparatively high monthly charge.
Other elements than credit score can aid in purchasing
If you have a credit score under 700 and are worried about getting approved, get ready by concentrating on your financial situation’s advantages. Remember, vehicle loans are frequently granted to persons with significant credit problems. Here are some good financial habits to mention in the finance department if you have bad credit.
Increase the down payment you offer.
Lowering your monthly payments can help you make up for a low credit score. In some cases, it can even result in a cheaper interest rate. Despite having a poorer credit score, a sizable down payment may make you seem less hazardous to some lenders.
Bring proof of your financial soundness.
If prospective lenders can see that you are stable in other aspects of your financial life, they are less likely to view you as a danger even if your credit score is low. Having confirmation of your residence and most recent pay stubs on hand to show lenders how long you have lived there and worked for your employer may make you appear more trustworthy.
Think about bringing your own funding
While dealerships may offer to finance, it’s also a good idea to check with your neighborhood bank or credit union. Even the rates for auto loans can be compared online. Once you’ve chosen your preferred lender, compare quotations from the best candidates and apply for preapproval to speed up the process.
Remember that obtaining financing will result in a “hard pull” on your credit. When comparing loan rates, it is beneficial to group applications together. Keep an eye on your credit scores if you end up with a loan with a higher interest rate than you desired. After six to twelve months of on-time payments, you may be able to refinance your auto loan at a lower interest rate.
Before you go car shopping, work on your credit.
If you’re still having trouble finding car loan rates that work for you, it may be time to postpone your car purchase and focus on improving your credit. This includes:
- Paying bills on time. A payment that is 30 days late can destroy your credit score, so pay at least the minimum on time.
- Maintaining low credit card balances in comparison to credit limits. Credit utilization refers to how much of your credit limit you are using, and it has a significant impact on your credit score. To improve your credit score, you can try a variety of strategies to reduce your credit utilization.
- Avoid credit applications within six months of applying for a car loan.
- Maintaining credit card accounts until there is a compelling reason to close them. Closing cards reduces your overall credit limit, which can have a negative impact on your credit utilization.
Your car loan can help you improve your credit.
Once you have a car loan, it will aid in the development of your credit in two crucial ways: payment history and credit mix. Your history of on-time bill payments is known as your payment history. It contributes more than any other single aspect to your credit score. The three main credit bureaus receive information from traditional lenders about your payments, which is used to create your credit ratings. (Note: Buy-here, pay-here lenders frequently fail to notify credit bureaus of payments. If payments are not reported, these loans won’t help you build credit and typically carry exorbitant interest rates.)
If you have both installment loans (with equal payments over a predetermined period of time) and revolving credit, your credit mix is considered (variable payments and no set end date, as with credit cards). Adding a car loan could raise your credit score if you mostly or only use credit cards.






